Self-sovereign identity gives users the ability to store and manage their own identity and data online. This new identity layer of the internet will fundamentally shift the relationship users have with the applications and services they interact with. When users access websites, they can provision access to their self-managed data, rather than relying on the company that operates said website to store and manage their personal information.
For example, we can use Bob, an everyday person who uses an ever-increasing number of different online applications and services for various purposes. If you're a human in the modern age reading this, you probably are like Bob in many ways. In the current model for identity on the internet, Bob's online data is stored in siloes across all the different servers for the companies he has accounts with.
Bob does not own this data—if his favorite photo-sharing social media application decides to shut down his account, he loses all of his memories stored there and the personal connections he has built over time. In a proposed future state of the internet powered by self-sovereign identity, Bob would own and manage all of his own data, then provision access to each of the applications and services whenever he chooses.
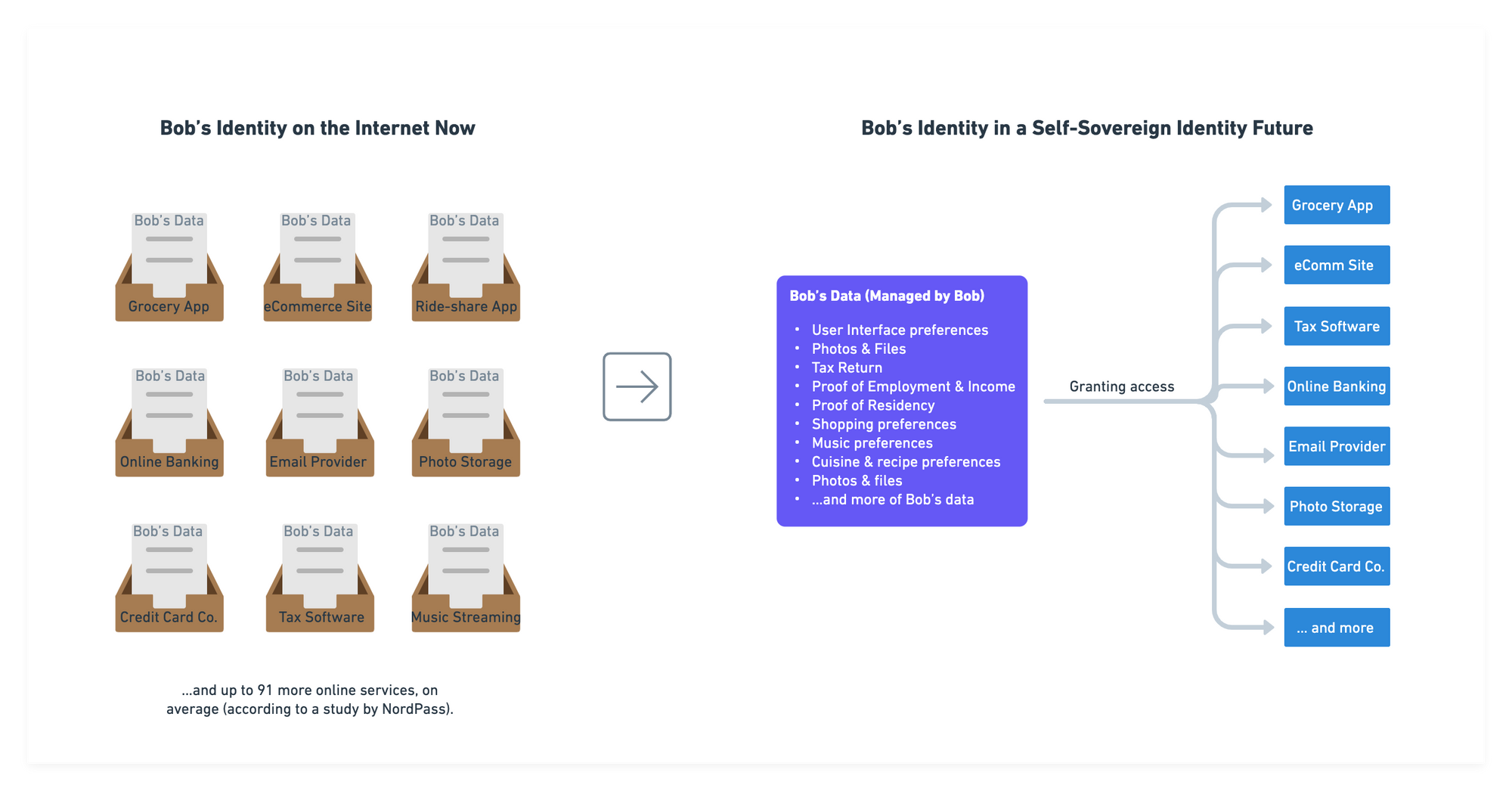
This shift has several benefits for both users and enterprises. For users, self-sovereign identity gives them more control over their personal data. They can choose which data to share and with whom, and they can revoke access at any time. This gives users greater privacy and security, while also improving user experience by allowing for more personalized experiences and reducing the number of unique usernames and passwords that need to be managed.
For enterprises and companies, self-sovereign identity has clear benefits–more personalized experiences for users, lower compliance costs associated with storing data, and reduced risks of data breaches.
Better User Experiences
By allowing users to share the data they choose, enterprises can create more tailored experiences that are relevant and engaging for the user. Providing highly personalized experiences can increase customer conversion rates, while also improving customer satisfaction and retention overall. A recent report from McKinsey found that companies that excel at personalization see 40% higher revenue than their competitors. Measuring performance across US industries, the report estimates that shifting to top-quartile performance in personalization would generate over $1 trillion in value. Current data aggregation practices to inform personalization strategies are incredibly costly, with billion-dollar companies specializing in collecting and selling customer data for personalization and targeted advertising.
With self-sovereign identity, we can enable a system where users themselves can selectively disclose their information for a more customized experience, which can increase conversion and retention rates while decreasing the costs of personalization. This may be a tough pill to swallow for companies earning millions (and billions, in some cases) by tracking and aggregating consumer data. However, leveling the playing field to restore user control of personal information will ultimately create unique branding and memorable experiences in the digital world.
Currently, our online preferences and behaviors are stored in siloes managed by separate companies. There are incredible opportunities unlocked if that data becomes portable. Users can then share a combination of their preferences and other identity attributes within a new application to customize their initial experience immediately. The key to remember here, however, is that the choice to share that information should remain with the user.
Reducing Compliance Costs
Decentralized identity can also help enterprises and companies reduce their costs of compliance. By storing less personal information of users on their servers, they can reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored and protected. This can lower costs associated with data management, in addition to reducing costs for maintaining compliance with various data protection regulations, like GDPR and CCPA.
GDPR (the General Data Protection Regulation) is a law passed by the EU, effective in May 2018, that enforces guidelines for any organization that targets or collects data related to people in the EU. PWC surveyed 200 C-Suite executives (CIOs, CISOs, CMOs, CPOs, and General Counsels) from US companies with more than 500 employees about their preparations for GDPR compliance in 2017 before the law became effective. The survey results showed that 68% of respondents had budgeted between $1 million and $10 million for GDPR compliance. Nine percent (9%) of the survey respondents expected to spend over $10 million to address GDPR obligations. The fines for violating the GDPR can be as high as the greater of €20 million or 4% of global revenues, plus damages owed to affected individuals seeking compensation.
Other jurisdictions, like the State of California, are following suit, passing their own versions of consumer data protection regulations in an effort to curtail the mass surveillance on citizens by Big Tech. The California Attorney General released an economic impact assessment, which estimated the total cost of initial compliance with the CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) would approach a staggering $55 billion. As regulators globally address public concerns about data privacy and processing, the costs for companies maintaining compliance will become even more significant, if they do not reframe their philosophy on the data collection practices at a fundamental level.
A new identity layer of the internet, which allows users to self-opt into disclosing their personal data and manage how their data are shared further, will significantly decrease the overhead and administrative costs associated with managing user data in company servers.
No Data to Breach
In addition to improved user experience and lower costs associated with data storage and compliance, self-sovereign identity can help prevent one of the biggest PR crises a large company can face–a data breach.
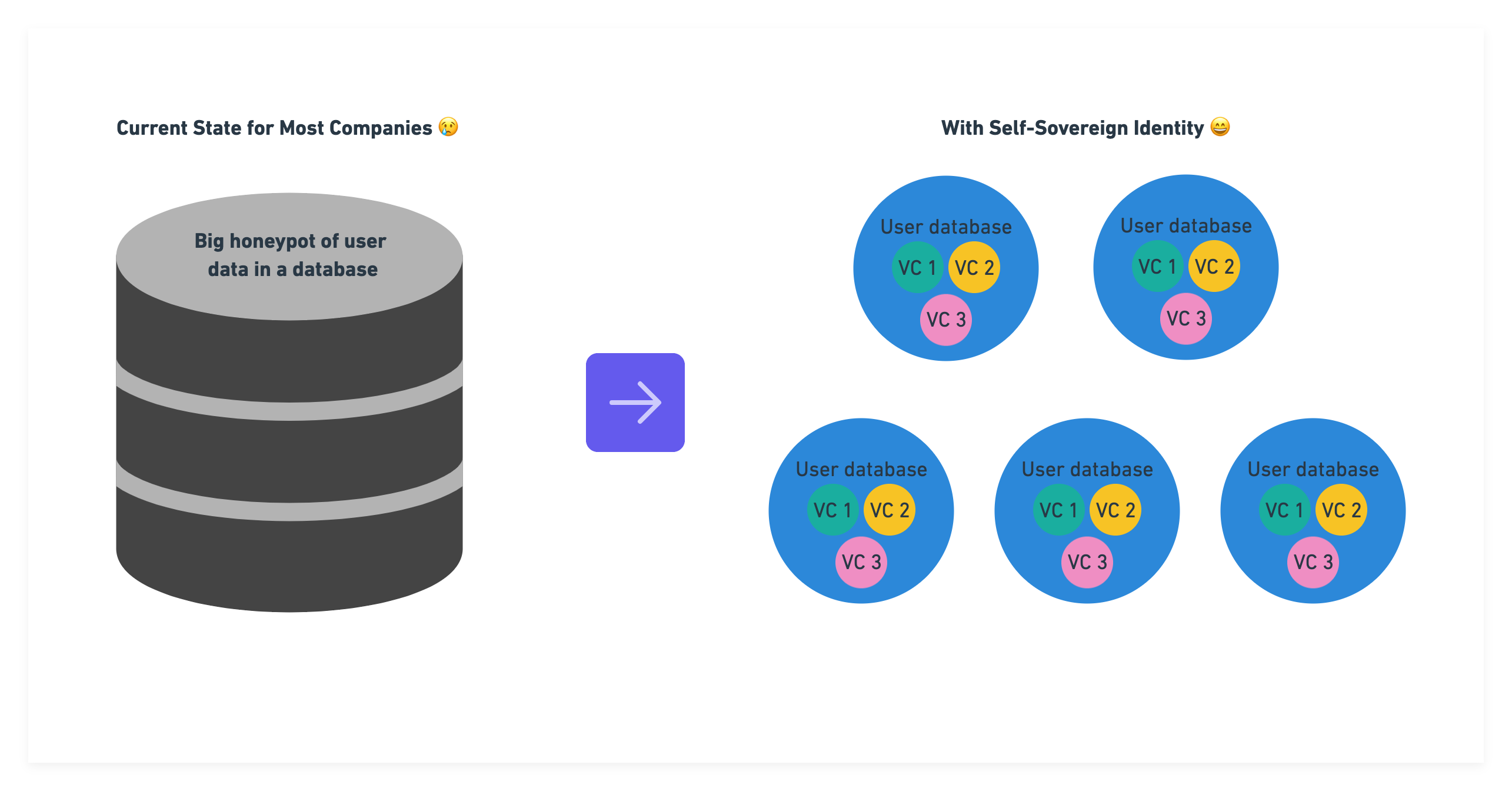
By reducing the amount of personally identifiable information (PII) on company servers, the honeypot of large internal databases storing millions of records representing user data, like names, addresses, passwords, and credit card details, is eliminated. This means that hackers will be less likely to target companies’ servers, and if they do, there will be less sensitive information for them to steal. While this also protects companies from the PR nightmare of a data breach, it also protects consumers by reducing the risks that their private information becomes compromised and potentially used for nefarious purposes.
The cost of data breaches can be significant for companies. According to a study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach for a company in the United States is $9.44 million, compared to the global average of $4.35 million. This total cost represents expenses such as legal fees, lost business, and damage to the company's reputation. For “mega-breaches” with between 50 to 60 million records affected, the average cost is $387 million.
In addition to the financial cost, data breaches can also lead to negative press and loss of consumer trust. McKinsey surveyed 1,000 consumers in North America and found that 71% of respondents would stop doing business with a company if it mishandled sensitive data. Data breaches can have a significant impact on a company's bottom line, as well as its reputation. This risk is mitigated in a new digital identity paradigm powered by verifiable credentials. If users are able to self-manage their data and provision access to websites only when needed, the data aren’t housed in centralized databases, which act as a honeypot for hackers or other bad actors looking to sell user credentials or data on the dark web.
Self-sovereign identity enabled by verifiable credentials can give users more control of their data online and afford them more customizable and personalized experiences as they interact with companies online, if they choose. Companies can see reduced compliance costs for enterprises and reduced risk of data breaches by reducing the amount of consumer data stored on their servers. By adopting self-sovereign identity solutions, companies can protect themselves and their customers from the significant costs and negative press associated with data breaches.
There is a wide range of industries that rely on data storage and record-keeping that can be supercharged with verifiable credentials and similar technologies. We previously wrote a blog post about how digital credentials can be applied within the healthcare industry. We will explore other industries in future blogs to come–so subscribe and follow along on this Verifiable Credentials Future State journey with us!
About Spruce: Spruce is building a future where users control their identity and data across all digital interactions.









